Castration in Dog: A case report KVK Anjaw.
A male dog (Splich Breed) of 5 month old, weighing 5 kg was brought to KVK, office Anjaw, with a chief complain that uncastrated dog are very difficult to keep in confined area after attending sexual maturity and also to prevent male reproductive related disease. Accordingly, castration was done on 16th Sept.2016, after following line of preoperative, during operation and postoperative procedure.
- Dog was physically examine for any abnormalities and disease
- As a preventive measure dog was under antibiotic coverage for 3 days prior to operation
- On the day of operation pet owner was asked to keep the dog on fast from early mooring and not to feed anything except water.
- Xylazine was used as sedative agents @ 1.5mg/kg BWT. I/M.
- Pelvic area in and around scortum, hair was clipped and shaved then painted with tincture iodine to disinfectant the area.
- Ketamin @ 7mg/kg Bwt I/V, was used as general anesthesia
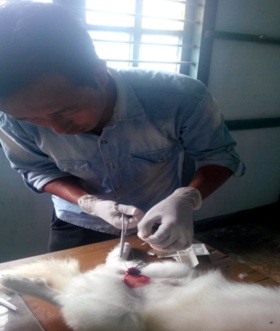
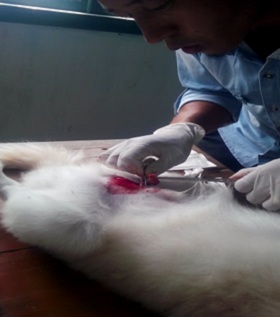
- Left testicle was slightly pushed towards abdomen from scrotal sac and incision was made just near scortum towards abdomen on the point of left testicle. Slowly layer after the incision was made, first skin is cut then layer covering testicle and ultimately testicle is exposed outside by gently application of pressure through cut mark. The vas deferens (spermatic cord), pampiniform plexus (vessels around the vas deferens), cremaster muscle, and arterial supply are clamped with artery forceps from both the side and strong ligation is applied with catguard (suture material), in the middle of clamped spermatid cord to prevent blood flow from either end, then spermatid cod is cut with BP blade near the point of tourniquet towards testicle to separate from rest of body. Cut end of large blood vessel and spermatid cord is crossed checked for bleeding and tincture iodine is applied before releasing the free end into the cavity.
- Similarly right testicles was removed from the same incision opening following similar sets of steps and procedure.
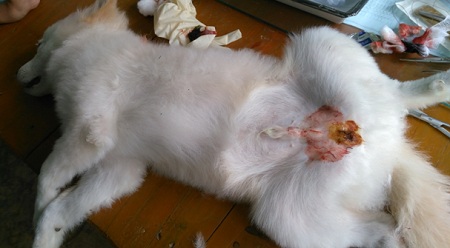
- Skin is sutured with black bedded suture material to apposed the skin and early healing of surgical wound.
- T.T injection of 1ml I/M was given as a preventive dose against tetanus.
- Postoperative care:
- Antibiotic continue for another 5 days
- Dressing of wound on alternate day with tincture iodine.
- Skin suture to be removed on 5th days of surgery.
Fig1. Exposed left testicle
Fig2. Legating spermatic cord
Fig3. Separating testicle with BP blade just above the point of legation
Fig4. Suturing skin
Fig5. After complete surgery